What You Need to Know about Data Consistency in Longitudinal Market Research: 2 Experts Weigh In
September 24, 2025
The State of Privacy Legislation with Howard Fienberg of The Insights Association
October 2, 2025It seems like generative AI has become ingrained in every aspect of life – but is that really the truth, or just a perception? While some platforms may have wide recognition, we wanted to understand what the true familiarity is of various generative AI tools among US consumers. In our recent round of research-on-research, we explored this.
Let’s dive into what we uncovered.
Overall
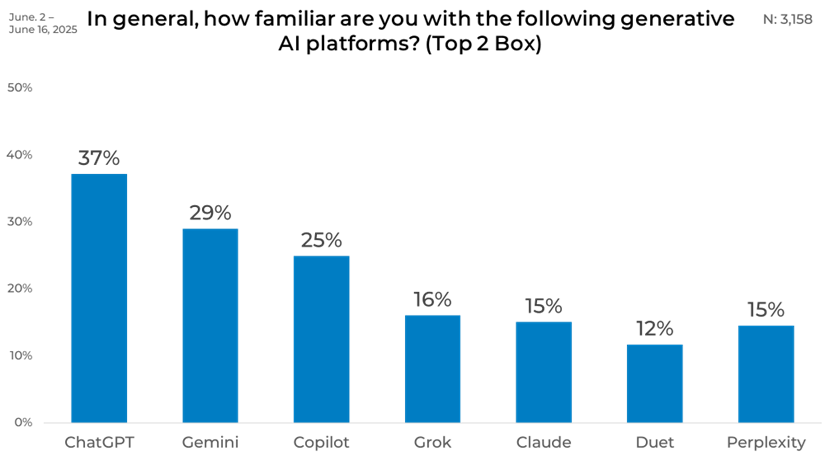
Overall, ChatGPT leads with 37% of respondents highly familiar with the platform. Gemini follows at 29%, while Copilot ranks close behind at 25%. Awareness of Grok, Claude, and Perplexity remains lower, with familiarity levels around 15 to 16%. Duet scores the lowest level of familiarity with 12%.
Wave-Over-Wave
Familiarity with generative AI platforms has steadily grown over the past year and a half. In Wave 1 just 23% of respondents were highly familiar with ChatGPT, but that figure has risen to 37% by Wave 5. Gemini and Copilot show similar upward trends, moving from 12% in to 25% most recently.
Growth is also visible among lesser-known platforms. Grok doubled its recognition, climbing from 7% in Wave 1 to 16% in Wave 5. Claude followed a similar trajectory, increasing from 7% to 15% across the same period. While overall familiarity remains lower for these tools, the steady rise across waves highlights a broadening base of awareness for the entire category.

Gender
Breaking down the data by gender, men reported higher familiarity of all generative AI platforms compared to women. Nearly half of men (49%) are highly familiar with ChatGPT, compared to just 27% of women. Similar gaps appear for Gemini (41% vs. 19%) and Copilot (36% vs. 15%). Even lesser-known platforms such as Grok and Claude draw more recognition from men than women. These numbers show a consistent trend of stronger awareness among men across the board.
Women’s lower familiarity is particularly evident with newer or niche platforms. While 27% know ChatGPT well, fewer than one in ten women report familiarity with Grok or Claude. By comparison, men’s awareness of these platforms is more than double.

Age
Age appears to have a strong correlation with familiarity regarding generative AI platforms. Younger adults report the highest awareness, with 56% of those aged 18 to 24 and 54% of those aged 25 to 34 familiar with ChatGPT. Percentages gradually decline with age, dropping to just 8% among those 65 and older. Gemini and Copilot follow a similar trend, with recognition peaking among younger respondents and declining sharply among older groups. Younger respondents also report greater exposure to newer platforms, such as Grok and Claude. Roughly one-quarter of adults under 45 are familiar with these tools, while fewer than 10% of adults over 45 report the same level of awareness.

Income
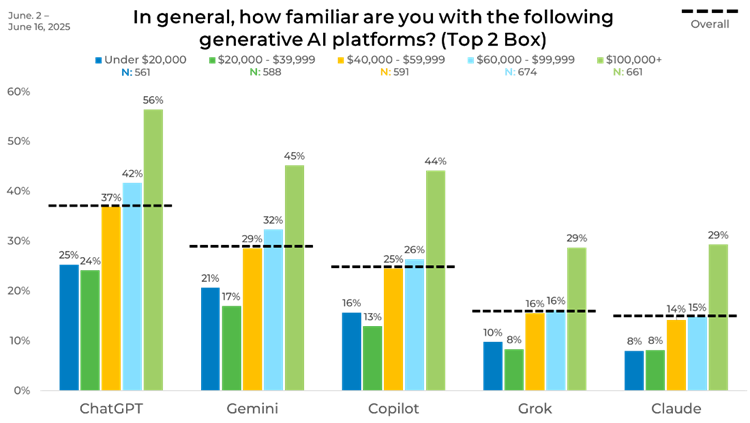
Income shows a clear correlation with familiarity. Among households earning $100,000 or more, 56% know ChatGPT well, compared to only 25% in the under $20,000 group. Gemini follows the same pattern, with awareness jumping from 21% in the lowest income bracket to 45% in the highest. Copilot familiarity doubles from 16% at the low end to 44% at the high end.
This gradient is also visible with smaller platforms. Grok and Claude are recognized by nearly 30% of higher-income households but only single digits of those with incomes below $40,000. The data points to a consistent link between higher income and broader awareness of generative AI platforms.
Political Affiliation
Political groups show subtle but meaningful differences in generative AI familiarity. Both Republicans and Democrats report equal familiarity with ChatGPT at 40 to 41%, while Independents and those with other affiliations are lower at 33% and 21%. Gemini familiarity mirrors this pattern, with Republicans and Democrats at 33% each, compared to smaller percentages among Independents and others.
Copilot, Grok, and Claude follow a similar breakdown. Republicans consistently show slightly higher recognition than Democrats for these tools, though the gap is relatively narrow. Independents and those with alternative affiliations consistently trail behind. Overall, political alignment does not appear to create wide divides, but stronger awareness is concentrated among the two major parties.

Region
Geographic differences are minimal compared to other demographics. ChatGPT familiarity is evenly spread, with the South slightly higher at 39% and the Midwest lowest at 32%. Gemini shows similar patterns, ranging from 24% in the Midwest to 31% in the West. Copilot scores peak in the South at 28% but stay relatively even across other regions.
Recognition of lesser-known platforms shows more fluctuation. Grok familiarity reaches 19% in the West but only 11% in the Midwest. Claude ranges between 11% and 17% depending on region. Despite these small shifts, regional awareness overall appears balanced.

Ethnicity
Familiarity also varies by ethnicity. ChatGPT familiarity is strongest among African American (49%), Asian (49%), and Hispanic (51%) respondents, compared to 33% of Caucasian respondents. Gemini exhibits a similar pattern, with higher recognition among minority groups compared to Caucasians. Copilot, Grok, and Claude follow the same distribution, with minority groups consistently reporting stronger awareness. For example, 32% of African Americans are familiar with Copilot, compared to 23% of Caucasians.

Panel
Panel results show notable differences depending on the sample source. Panel H reports the highest familiarity, with 53% familiar with ChatGPT and 49% with Gemini. In contrast, Panel J and Panel P are much lower: ChatGPT drops to around 30%, and Claude recognition falls below 10%. The widest gap appears between Panel H and Panel J, where Gemini familiarity ranges from nearly half of respondents down to just 16%.

These contrasts highlight the importance of strategically blending panels. Examining a single panel alone can create misleading impressions, while combining them provides a more transparent and more balanced view of platform familiarity.
To learn more about EMI’s Strategic Sample Blending approach and how it can ensure your study is not impacted by sample selection bias, click the button below.




