How Many AI Tools Can You Name? The Current State of AI Familiarity with US Consumers
December 17, 2025
The 2025 Recap
December 30, 2025We’ve kept a close pulse on consumer familiarity and usage of generative AI platforms since ChatGPT entered the mainstream in November 2022 via our quarterly research-on-research. In part two of our series on AI familiarity and usage with US consumers, we shift the focus to generative AI usage. (You can read part 1 here.)
Let’s see what we uncovered.
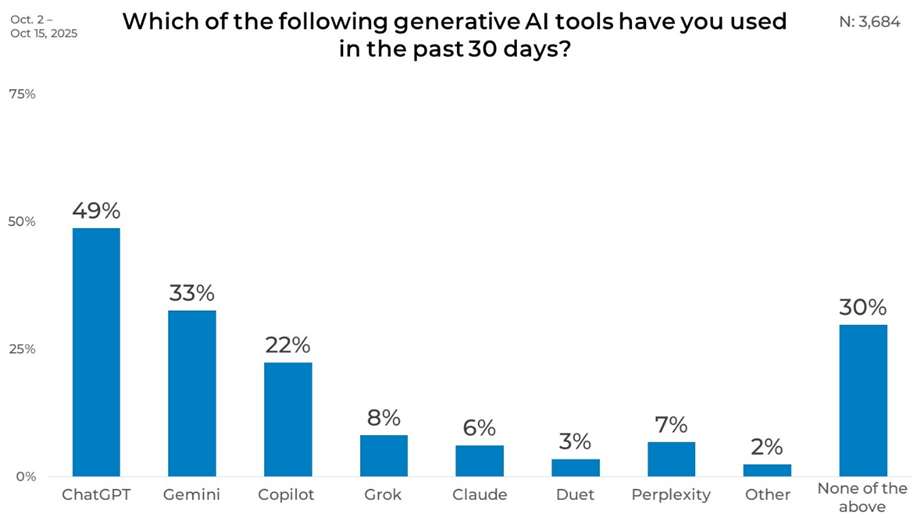
Overall
Unsurprisingly, ChatGPT led in recent usage with 51% of respondents reporting they have used it in the past 30 days. Gemini follows at 39%, while Copilot reaches 23%. Usage drops sharply for smaller platforms, with Perplexity at 10%, Grok and Claude each at 8%, and Duet at 4%. Notably, 26% of respondents report not having used any of the listed tools in the past month, indicating that active use still lags behind overall awareness.
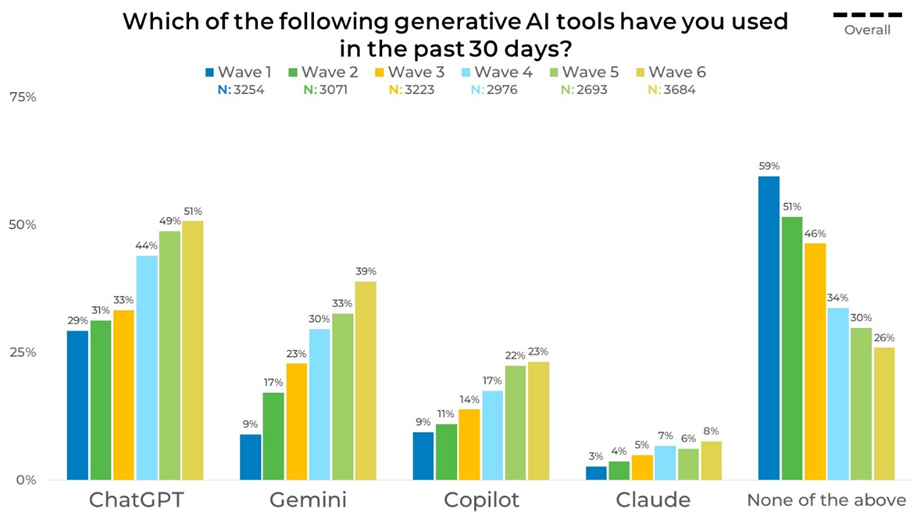
Wave-Over-Wave
Similar to how familiarity has grown wave-over wave, usage has increased steadily across waves, particularly for leading platforms. ChatGPT usage rises from 29% in Wave 1 to 51% by Wave 6, showing consistent growth over time. Gemini follows a similar trajectory, increasing from 9% to 39%, while Copilot grows from 9% to 23%. At the same time, the share reporting no use of the tools declines sharply from 59% in Wave 1 to 26% in Wave 6, reflecting broader adoption of generative AI tools.
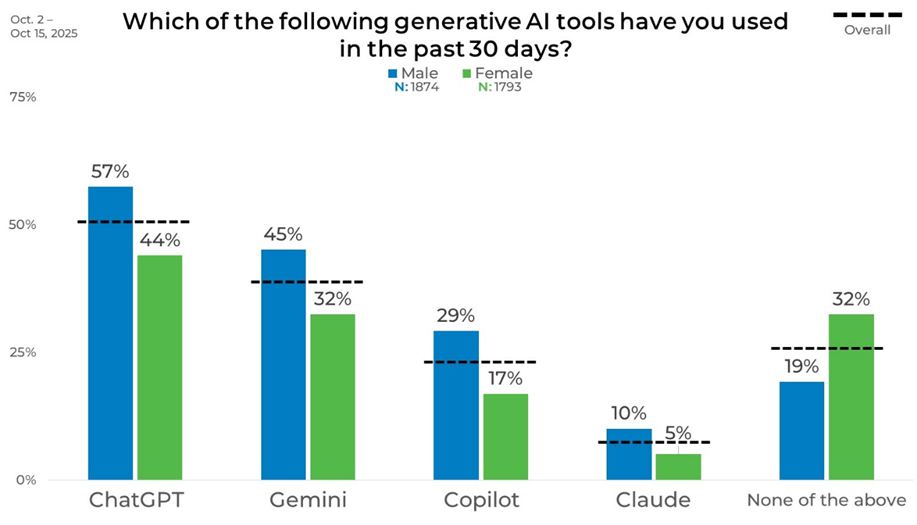
Gender
Looking at the data by gender, men report higher recent usage than women across all measured platforms. ChatGPT is used by 57% of men compared with 44% of women, while Gemini shows a similar gap at 45% versus 32%. Copilot usage stands at 29% among men and 17% among women, and Claude usage remains relatively low for both at 10% and 5%, respectively. Women are also more likely to report no recent usage, at 32% compared with 19% among men.
Age
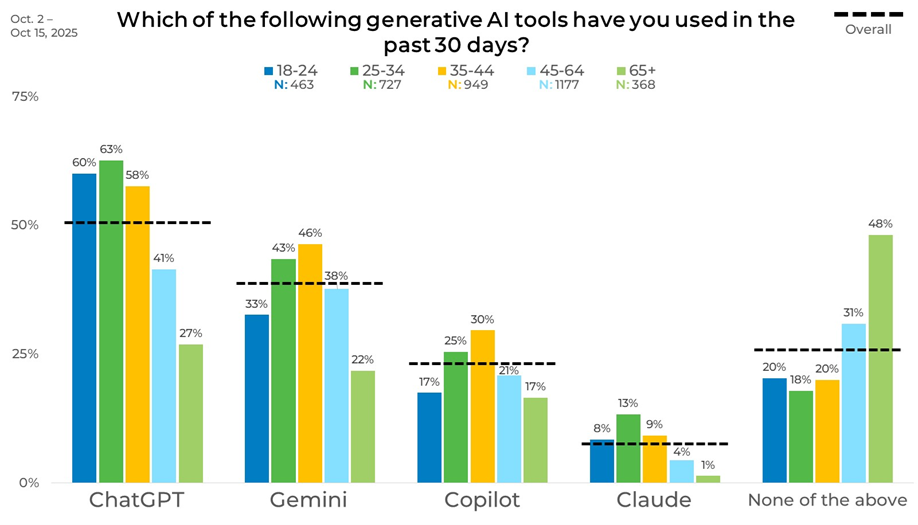
Younger adults report the highest levels of recent usage across platforms. ChatGPT usage reaches 60% among those aged 18–24 and peaks at 63% among those aged 25–34. Gemini usage stands at 33% among 18–24-year-olds and increases to 43% among those aged 25–34, while Copilot reaches 17% and 25% in these same age groups.
Usage declines with age, particularly among older adults. ChatGPT usage drops to 41% among those aged 45–64 and falls further to 27% among those aged 65 and older. Gemini usage follows a similar pattern, declining from 46% among 35–44-year-olds to 22% among those 65 and older. Nearly half of respondents aged 65 and up report no recent usage, at 48%.
Income
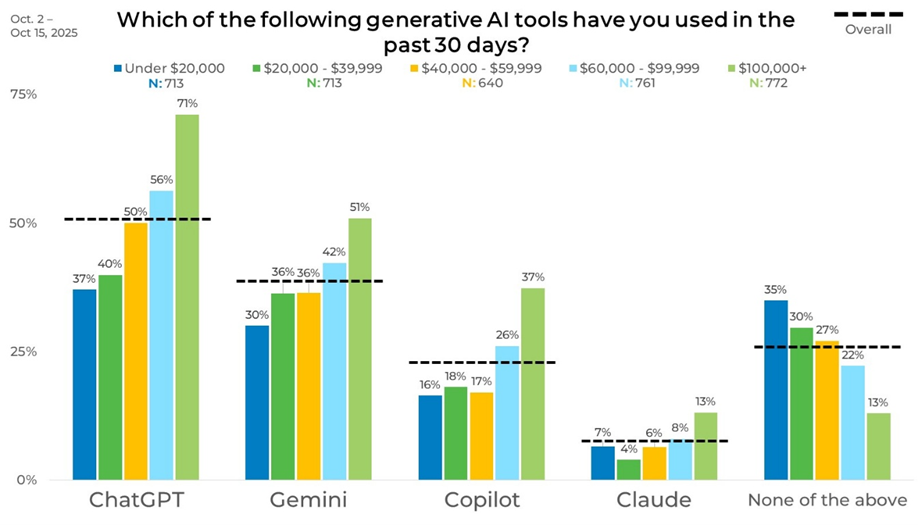
Recent usage increases steadily with income. ChatGPT usage rises from 37% among those earning under $20,000 to 71% among those earning $100,000 or more. Gemini grows from 30% to 51% across the same income range, while Copilot increases from 16% to 37%. Higher-income respondents consistently report greater engagement across platforms.
Lower-income respondents are more likely to report no recent usage. Among those earning under $20,000, 35% report not using any of the listed tools in the past 30 days, compared with 13% of those earning $100,000 or more. Use of smaller platforms such as Claude also increases with income, rising from 7% to 13% across income brackets.
Political Affiliation
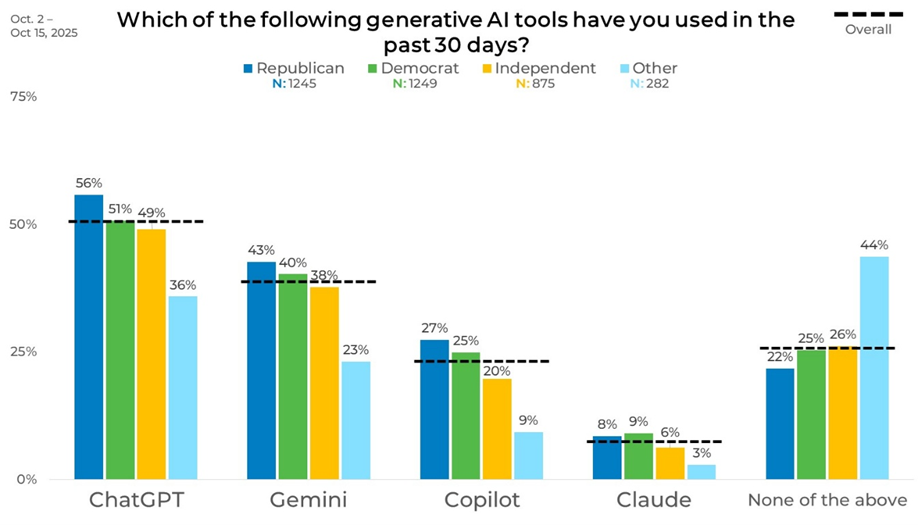
Recent usage varies by political affiliation, though the overall ranking of platforms remains consistent. ChatGPT usage reaches 56% among Republicans and 51% among Democrats, compared with 49% among Independents and 36% among those identifying as Other. Gemini usage ranges from 43% among Republicans to 23% among Other respondents. Those identifying as Other are most likely to report no recent usage, at 44%, compared with roughly one-quarter among other groups.
Ethnicity
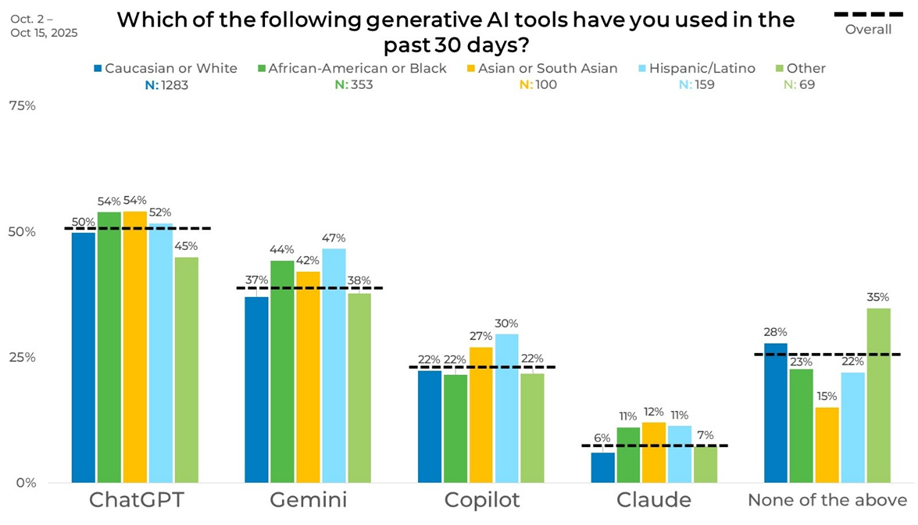
Exploring the data by ethnicity highlighted the relatively high engagement among African American, Asian or South Asian, and Hispanic/Latino respondents. ChatGPT usage reaches 54% among both African American and Asian or South Asian respondents and 52% among Hispanic/Latino respondents, compared with 50% among Caucasian respondents. Gemini usage follows a similar pattern, peaking at 47% among Hispanic/Latino respondents.
Differences are also visible for other platforms. Copilot usage reaches 30% among Hispanic/Latino respondents, compared with 22% among Caucasian respondents. Claude usage is higher among African American, Asian or South Asian, and Hispanic/Latino respondents, each at around 11–12%, compared with 6% among Caucasian respondents. Caucasian respondents are also more likely to report no recent usage, at 28%.
Panel
Panel results show meaningful variation in reported usage. ChatGPT usage ranges from 36% in Panel F to 71% in Panel U, while Gemini ranges from 33% in Panel A to 55% in Panel U. The share reporting no recent usage also varies widely, from 11% in Panel U to 38% in Panel F. These differences highlight how individual panels can skew usage estimates.
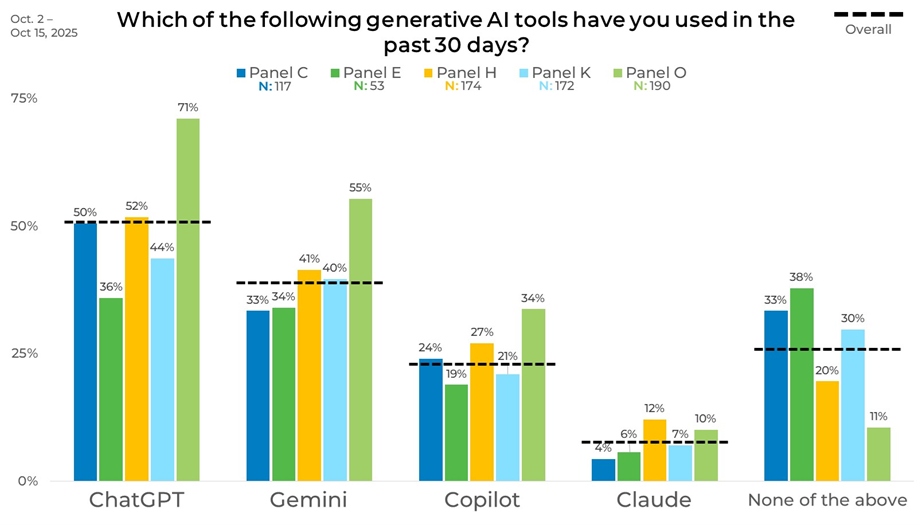
This is a good reminder that how you build your sample really matters. Strategic blending helps avoid the bias that can sneak in when you don’t understand the attitudes and behaviors of the panels you use.